Still have questions? Leave a comment

Checklist: Dissertation Proposal
Enter your email id to get the downloadable right in your inbox!

Examples: Edited Papers
Enter your email id to get the downloadable right in your inbox!
Need
Editing and
Proofreading Services?

What is a Noun? Definition, Types & Examples
 Apr 27, 2025
Apr 27, 2025 6
min read
6
min read
eyWhether we are speaking, reading, listening, or writing, nouns are an inseparable part of our daily life. Knowing what’s a noun is very important to communicate effectively. In this article, we will decode the definition of nouns.
We will introduce the concept of ‘generic nouns’, which represent entire categories of things, highlighting their grammatical flexibility and contextual usage.
We will also understand various types of nouns with the help of simple examples. Whether you’re a language enthusiast or someone looking to deepen their grammar knowledge, this article will make understanding nouns easier for everyone. Let’s start with an easy noun definition.
What is a Noun?
A noun is defined as a word that names or identifies a person, place, thing, idea, or animal.
Nouns are the words in a sentence that represent a certain person (John), place (London), thing (pen), idea (discipline), or animal (dog). Th can be concrete (pen) or abstract (discipline).
Nouns can be categorized into different categories, such as common nouns, proper nouns, collective nouns, count nouns, and mass nouns.
The easiest way to spot a noun is by identifying a name, place, thing, idea, or animal in a sentence.
Being aware of the noun definition, noun meaning, and what are nouns is integral for understanding grammar and sentence structure in any language.
A list of nouns commonly used is:
Animal: Cat
Place: Park
Thing: Bicycle
Person: Girl
To understand the meaning of nouns in detail, let’s take a look at some more examples of nouns.
Noun examples
1. Nouns naming a person:
A man
A postman
The Prime Minister
Indira Gandhi
2. Nouns naming a place
My house
A mall
India
Mount Fuji
3. Nouns naming a thing
A pen
A baseball
A chair
The magical book
4. Nouns naming an idea
Justice
Freedom
Loyalty
Creativity
5. Nouns naming an animal
A dog
A cat
A cow
A tiger
These examples give us a quick insight into the process of identifying and choosing nouns in a sentence. Nouns are one of the eight parts of speech that play a vital role in forming sentences.
What are parts of speech?
Parts of speech are specific roles and functions of a word in the English language. Noun, verb, adjective, adverb, pronoun, preposition, conjunction, and interjection are the eight parts of speech.
Types of nouns
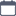
1. Proper noun
These are nouns that specifically name a person, place, or thing. Proper nouns start with capital letters, making it easy to distinguish them from other types of nouns.
Some proper noun examples are:
The time we visited Delhi was one of the most fun times of my life. (Name of a particular place.)
I watched a film about Freddie Mercury. (Name of a particular person.)
I love shopping at Shopper’s Stop. (Name of a particular brand.)
2. Collective noun
A noun used to refer to a group of individuals, animals, or things as a single unit is called a collective noun. It shows a grouping of similar things. Collective nouns are a type of singular noun, but they represent a plurality of items.

Some collective noun examples are:
A deck of cards.
A class of students.
A hive of bees.
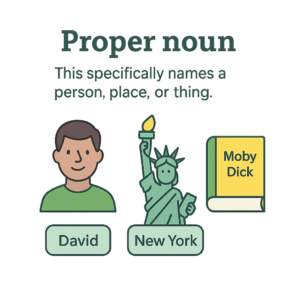
3. Common noun
A common noun refers to a general category of people, places, or things. Common nouns do not represent a particular category or specific instance.
Some common noun examples are:
I am going to the hospital. (place)
I like using a pencil to sketch. (thing)
I bought a new car. (item)
4. Abstract noun
A word that represents an idea, a state, or an intangible concept is called an abstract noun. Abstract nouns are things that cannot be seen or touched physically but are present as feelings or emotions. Abstract nouns refer to things that are intangible and exist as feelings, thoughts, and ideas.
Some abstract noun examples are:
Honesty is the best policy.
Loyalty is a dog’s best trait.
Freedom must not be considered as a liberty.
5. Concrete noun
A concrete noun is a type of noun that refers to tangible objects that can be felt or perceived physically using their senses. Unlike abstract nouns, concrete nouns can be seen, touched, heard, and experienced physically.

Some concrete noun examples are:
The tree was 100 years old.
The family traveled by bus.
I want to read a book.
6. Plural noun
A plural noun is used to indicate more than one of a place, thing, person, animal, or idea. Plural nouns are represented by words that are made plural by adding ‘s’, ‘es’, or ‘ies’ to the ending. Confusing plural nouns with collective nouns is one of the common grammatical mistakes people make. Plural nouns refer to multiple individuals or objects, while collective nouns refer to a group or collection of individuals or objects.

Some plural noun examples are:
We bought a few oranges from the market yesterday.
There were a lot of dishes to be cleaned.
All the candies were sweet.
7. Possessive noun
A possessive noun is a word used to indicate ownership or possession of something. It shows possession or that something belongs to someone. It is often formed by adding a ‘s at the end of the words, which shows that the noun owns or possesses something.
Some possessive noun examples are:
The king’s reign was over. (Reign of the king)
Students’ assignments were submitted. (Assignments belonging to the students)
All the car’s windows have to be shut. (Windows belonging to the car)
8. Compound noun
A noun that is formed by combining two or more words to create a new, single noun is called a compound noun. The combination of these two or more words results in the formation of a new word having a distinct meaning. The three types of compound nouns that are commonly used are hyphenated compound nouns, closed compound nouns, and open compound nouns.

Some compound noun examples are:
Bus stop (bus + stop) (open compound noun)
Classroom (class + room) (closed compound noun)
Mother-in-law (hyphenated compound noun)
9. Countable nouns
Countable nouns, also known as count nouns, are people, objects, places, things, and ideas that can be counted using numbers. These nouns have plural forms.

Some examples of countable nouns are:
He purchased two dozen apples for his family. (apple + s)
She borrowed two purses from a friend. (purse + s )
There are many temples in India. (temple + s)
10. Uncountable nouns
Uncountable nouns, also known as mass nouns, are those objects and ideas that cannot be counted using numbers. This means that the individual units of these nouns cannot be counted. These nouns do not have plural forms. Words such as some, any, much, and enough can be used to describe the quantity of these nouns.
Some examples of uncountable nouns are:
Trees grew in abundance. (Individual units of “abundance” cannot be counted.)
She has vast knowledge in her field. (Individual units of “knowledge” cannot be
counted.)
She appreciated her tolerance. (Individual units of “tolerance” cannot be counted.)
11. Appositive nouns
Nouns that are used to add specificity or additional context to a noun in the sentence are known as appositive nouns. Appositive nouns give extra information about the subject and make sentences more engaging. They are typically set off by commas, dashes, or parentheses.
Some of the examples are:
The country, India, is known for its culture. (“India” serves as an appositive noun that renames “the country.”)
My dog, Leo, loves to play fetch. (“Leo” serves as an appositive noun that renames “my dog.”)
My sister, Riya, is a dancer. (“Riya” serves as an appositive noun that renames “my sister.”)
Using nouns as different parts of a sentence
Noun as a subject
The subject of a sentence is the noun or noun phrase that performs the main action of the sentence or is the main focus of the sentence. A subject can be easily identified by asking the question “who?”. It mostly appears at the beginning of a sentence when used as a subject.
Examples:
The baby was crying. (Who was crying? – the baby)
Cyrus was a naughty child. (Who was a naughty child? – Cyrus)
Mother went to the store. (Who went to the store? – mother)
Noun as a subject complement
A noun or noun phrase serves as a subject complement when it follows a linking verb and provides additional information about the subject in the sentence. The subject is typically described or renamed by a subject complement.
Examples:
The painting was a masterpiece. (“A masterpiece” describes the subject, “the painting.”)
He is a scientist. (“A scientist” renames and describes the subject “he.”)
The owner of this house is Alan. ( “Alan” identifies the subject, “the owner.”)
Nouns as subject complements help provide more information about the subject, clarifying its identity, characteristics, or state. They are an important element in sentences that use linking verbs to connect to the subject.
Noun as an object
When a noun is placed in a position where it receives the action of the verb, it is used as an object. An object placed immediately after a verb is known as a direct object. An object can be easily identified by asking questions like “what?” or “whom?”.
Examples:
Izzy loved her skirt. (What did Izzy love? – her skirt)
The baby wanted milk. (What did the baby want? – milk)
Father drove the car. (What did father drive? – the car)
Noun as an object complement
A noun or noun phrase functions as an object complement when it follows a direct object and provides further description or identification of that object. The object is typically described or renamed by an object complement.
Examples:
He painted the wall red. (“red” is the object complement, describing the object “wall.”)
We named our baby Judy. (“Judy” provides additional information about the object “baby”)
She considered the book a good read. (“A good read” describes the object “book.”)
Noun as a modifier
Nouns that act as an adjective and provide additional information or context about another noun are referred to as modifiers. They are also called attributive nouns. Nouns can modify other nouns, acting in various grammatical roles such as complements, object complements, and attributive nouns. They function similarly to adjectives but maintain their classification as nouns, emphasizing their importance in sentence structure and noun phrases.
Examples:
The mechanic understood that the car engine was faulty. (“car” acts as a modifier for “engine” and indicates that this type of engine is used in a car)
She took her Labrador Retriever to the dog park. (“dog” acts as a modifier for “park” and indicates that this type of park is for dogs)
He threw his coffee cup in the dustbin. (“coffee” acts as a modifier for “cup” and indicates that this type of cup is for coffee)
We hope that the given examples will help you use nouns effectively while communicating. As language experts who provide proofreading services, we’d love to help you perfect your words.
Bookmark PaperTrue’s Resource Centre for useful grammar tips!

Tanvi

With a foundation in Life Sciences, Tanvi enjoys curating technical writing tips tailored for ESL students. When she's not translating complex concepts into bite-sized nuggets, she can be found playing with dogs or painting landscapes.
4 comments on “What is a Noun? Definition, Types & Examples”
Comments are closed.




Found your website helpful for improvising my English language & it is easy to understand as well
Found your website helpful
I really did appreciate this site, l read and learnt alot.
I really did appreciate your site, l found it helpful.
Thanks aton.