Still have questions? Leave a comment

Checklist: Dissertation Proposal
Enter your email id to get the downloadable right in your inbox!
[contact-form-7 id="12425" title="Checklist: Dissertation Proposal"]
Examples: Edited Papers
Enter your email id to get the downloadable right in your inbox!
[contact-form-7 id="12426" title="Examples: Edited Papers"]Need
Editing and
Proofreading Services?

What are Pronouns? Meaning, Usage, Types, & Examples
 Jun 08, 2025
Jun 08, 2025 8
min read
8
min read
Pronouns are words that replace a noun or pronoun in a sentence, and they can also substitute for entire phrases or noun phrases to avoid repetition and improve clarity. The use of pronouns is meant to make language more concise and easier to understand. Pronouns are important for daily communication. In this article, learn everything about pronouns. From the pronoun definition to the types, we’ve explained everything with examples.
There are many different pronoun types in English grammar, each serving a unique purpose. These different types of pronouns are classified based on their function and usage in sentences. Many pronouns can take different forms depending on gender, number, or case, and pronouns refer to specific nouns or noun phrases called antecedents.
We’ve also given the rules for using pronouns. So without delaying further, let’s begin!
What is a pronoun?
A pronoun is a word that is used instead of a noun. Pronouns enable us to refer to someone/something without using their name repeatedly. It is one of the important parts of speech in English.
Here is an example to understand this pronoun definition:
John is sleeping. He will wake up at 8 am.
Here, the word “he” is used to refer to John. “He” helps to communicate about “John” without unnecessarily repeating the word “John”.
These pronouns can be further categorized into subject and object pronouns. Let’s explore these concepts very quickly!
What are subject pronouns?
Pronouns that indicate the subject of a sentence (who is performing the action) are known as subject pronouns. I, we, you, he, she, it, they are examples of subject pronouns.
For example:
I ate a chocolate
In this sentence, I is the subject pronoun performing the action.
What are object pronouns?
Pronouns that are affected by the action performed in a sentence are known as object pronouns. An object pronoun is a pronoun that receives the action of the verb or is the object of a preposition. Me, us, you, him, her, them, and it are some examples of object pronouns.
For example:
We told them everything
In this sentence, “them” receives the action of telling by the pronoun “we”. The direct object is the noun or pronoun that receives the action of the verb; in this case, “them” is the direct object. For example, in “She saw him,” “him” is the direct object. An indirect object is the recipient of the action, typically positioned between the verb and the direct object, as in “She gave him a gift,” where “him” is the indirect object.
After understanding what is a pronoun, let’s understand its types!
Types of pronouns
1. Personal pronouns
The pronouns that refer to specific people or things are known as personal pronouns. Some examples of personal pronouns are I, you, he, she, it, they, we, and you.
Depending on the point of view (first person, second person, or third person, the forms of personal pronouns can change. Personal pronouns have different forms depending on gender, number, and case. Let’s see a table to understand these concepts better.
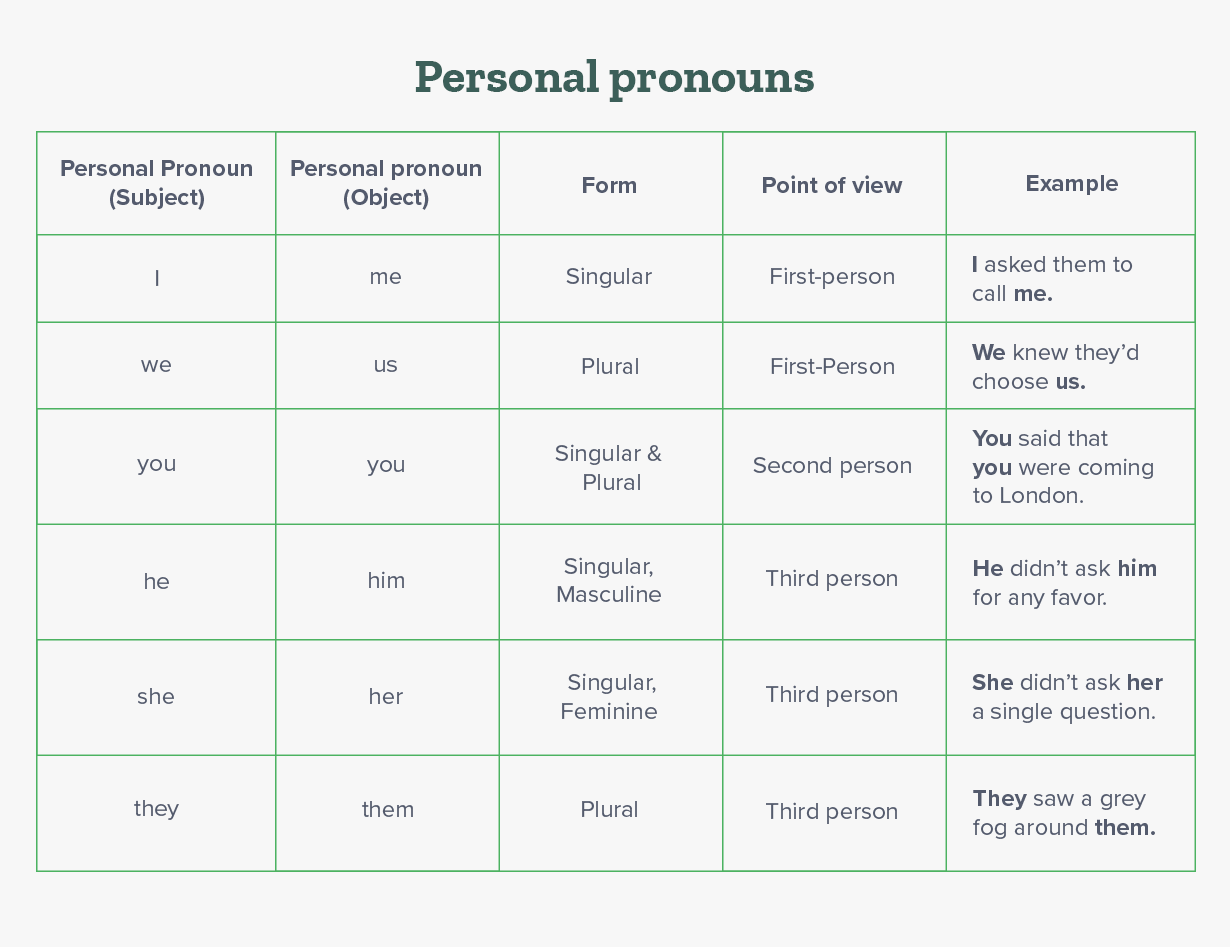
Now let’s understand what is a demonstrative pronoun.
2. Demonstrative pronouns
The words that are used to point out or refer to particular persons, places, things, or ideas are known as demonstrative pronouns. Demonstrative pronouns can also be used to refer to a specific person in a sentence. Some commonly used demonstrative pronouns are: that, this, these, and those.
Here are some examples of pronouns in sentences:
That is my book.
This is the correct file.
These apples are ripe.
Those pencils are not mine.
Let’s move on and know more about what is an indefinite pronoun!
3. Indefinite pronouns
Common Indefinite pronouns are words used to refer to people or objects that aren’t clearly defined or specified by name or any other feature. These pronouns refer to no particular person or thing, emphasizing their general and non-specific nature in sentences. These vague pronouns are usually used when the nouns are unknown, or unimportant.
Commonly used indefinite pronouns include some, any, none, nobody, someone, anyone, no one, nothing, everyone, everybody, everything, nothing, other, others, few, all, any, each. Many indefinite pronouns require singular verbs when they are used as the subject.
Following are some pronoun examples to understand them better:
He saw no one in the living room.
I told him everything.
She was talking about other people she met.
4. Reciprocal pronouns
The pronouns that show a connection between two or more people or things are known as reciprocal pronouns. These pronouns describe a mutual relationship or reciprocal relationship, where actions or feelings are exchanged equally between the entities involved. Some examples of reciprocal pronouns are each other and one another.
Browse through the following examples of reciprocal pronouns:
We supported each other in difficult times.
They told one another the truth.
They discussed the topic with each other.
Now, let’s see what is a reflexive pronoun!
5. Reflexive pronouns
The pronouns formed by adding “self” or “selves” to existing pronouns are known as reflexive pronouns. While “self” is added to create a singular pronoun, “selves” indicates a plural pronoun.
Some examples of reflexive pronouns are: myself, yourself, himself, yourself, itself, yourselves, themselves, oneself, ourselves
The sentences given below accurately demonstrate how to use these pronouns:
They congratulated themselves on a job well done.
He taught himself how to play the guitar.
She bought herself a new dress for the party.
After understanding reflexive pronouns, let’s explore what is an intensive pronoun!
6. Intensive pronouns
The pronouns that focus on or strongly emphasize the noun or other pronouns in the sentence are known as intensive pronouns. They are similar to reflexive pronouns. Using two sentences can help clarify the use and emphasis of intensive pronouns in writing.
Here are some pronoun examples in sentences to understand them:
The students themselves didn’t understand the assignment.
The president himself will be attending the event.
I, myself am not happy with the changes.
7. Interrogative pronouns
The pronouns that are used to ask questions are called interrogative pronouns. Some examples of interrogative pronouns are who, whom, whose, what, and which. Let’s see how to use these pronouns in sentences:
Who is that girl?
Whose bag is this?
Which is the best design of these?
8. Distributive pronouns
The pronouns that help to separate or distribute the members of the group are known as distributive pronouns. They help to refer to individual members of a group.
Some examples of distributive pronouns are either, each, neither, every, any, and none.
Read the following sentences to understand their usage:
Each student in the history class received a textbook.
Neither of the candidates impressed the committee.
Every student must submit their assignment by Saturday.
Now, let’s move on and understand what is a possessive pronoun.
9. Possessive pronouns
The pronouns that indicate ownership or show that something belongs to someone are called possessive pronouns. Some examples of possessive pronouns are my, your, his, her, its, our, their, yours, ours, theirs, hers, mine
The following sentences demonstrate their usage:
This is my pen.
We went in his car.
I wanted to click their picture.
10. Relative pronouns
Relative pronouns introduce a relative clause, giving more information about other nouns/pronouns in the sentence and connecting parts of a sentence. They help to create complex sentences.
A relative pronoun is a word like who, whom, which, whose, or that that introduces a relative clause and provides additional information about a noun. Relative clauses often connect to independent clauses to add extra information within a sentence.
Some examples of relative pronouns are who, whom, which, whose, and that. Here are some sentences to understand relative clauses better:
The girl who arrived was not Mary’s real sister.
I know that life isn’t easy.
He knew whom to call.
After understanding what are pronouns, let’s understand the rules for using them! These rules will help you use pronouns with other nouns, verbs, adjectives, conjunctions, and adverbs.
Pronoun Usage
Pronouns are used to substitute nouns in a sentence, making our language less repetitive and more concise. Depending on their role in the sentence, pronouns can act as subjects, objects, or complements. For example, personal pronouns like “I,” “you,” and “they” are used to refer to the speaker, the person being addressed, or other people, respectively. Possessive pronouns, such as “mine,” “yours,” and “theirs,” show ownership or possession. Indefinite pronouns like “someone,” “anybody,” and “everyone” are used to refer to people or things in a general or non-specific way. The form of a pronoun may change depending on its function in the sentence and the context in which it is used. By choosing the correct pronoun form, we ensure our sentences are clear and grammatically correct.
Essential rules while using pronouns
1. Pronoun-antecedent agreement: The pronoun used must have the same form as the noun it is referring to. This means that if the noun is singular, the pronoun must also be singular, and if it’s plural, the pronoun must also be plural.
For example:
They ate apples.
I bought a wooden box.
Here, “they” and “apples” are plural whereas both “I” and “box” have a singular form.
This rule also means that the pronoun must have the same gender form as the noun it refers to.
For example:
John told George about his painful story.
Rita gave a watch to her sister.
In the first sentence, “his” is a masculine pronoun used to describe the masculine subject “John”. In contrast, in the second sentence, “her” is a feminine pronoun used to describe the female subject “Rita”.
2. Understand context while using pronouns: For example, use reflexive pronouns when the subject and the object refer to the same person or thing.
For example:
She did all the work herself.
They cleaned the room themselves.
3. Use gender-neutral pronouns: If you’re unsure about gender, to ensure clarity, use gender-neutral pronouns like “they”, “them” and “their” to refer to a group of people.
For example:
They attacked the village.
It was their problem.
4. Avoid ambiguous references: Be careful not to use vague pronouns that could have multiple interpretations leading to ambiguity.
For example:
John told Michael that he should now study.
In this sentence, it’s unclear whether John should now study or Michael. To avoid ambiguity, a better sentence is:
John told Michael that Michael should now study.
Pronoun Antecedents
A pronoun’s antecedent is the noun or noun phrase that the pronoun replaces in a sentence. The antecedent usually appears before the pronoun, providing context for what or whom the pronoun refers to. For example, in the sentence “The teacher gave her students homework, and they completed it on time,” the antecedent for “they” is “students,” and the antecedent for “it” is “homework.” Sometimes, the antecedent may be implied or appear after the pronoun, depending on the sentence structure. Understanding the relationship between pronouns and their antecedents is important for clarity, as unclear or ambiguous antecedents can make sentences confusing. Always ensure that each pronoun clearly refers to a specific noun or phrase in the context of your writing.
Pronouns and Gender
Pronouns can be used to refer to individuals of different genders, and their usage in English grammar has evolved to become more inclusive. Traditionally, personal pronouns like “he” and “she” have been used to refer to males and females, respectively. However, as our understanding of gender has grown, so has the language we use. Many people now use gender-neutral pronouns such as “they” and “them” as singular pronouns to refer to someone whose gender is unknown, unspecified, or non-binary. Using the correct pronouns to refer to people is an important way to show respect and inclusivity. In both spoken and written English, it is essential to use the pronouns that individuals prefer, as this helps create a more welcoming and understanding environment for everyone.
This concludes our guide to pronouns! You can create a pronouns list and jot down the pronouns for future reference. With this, you can also briefly define pronoun types and mention rules after the pronouns list. This list of pronouns will help you to communicate effectively.
After understanding what are pronouns, you can use them while speaking and writing. An important step you need to take after writing is editing. As experts in editing and proofreading services, we’d love to help you perfect your text!
Here are some other useful resources for you: