Still have questions? Leave a comment

Checklist: Dissertation Proposal
Enter your email id to get the downloadable right in your inbox!

Examples: Edited Papers
Enter your email id to get the downloadable right in your inbox!
Need
Editing and
Proofreading Services?

What Is Sentence Structure? Meaning, Types & Examples
 May 07, 2024
May 07, 2024 5
min read
5
min read
Sentence structure is the way words are put together in a sentence to convey meaning. It involves placing subjects, verbs, and objects in a specific order to communicate clearly. Dive in to understand everything about the rules and types of sentence structure!
We’ve also included practical sentence structure examples for you. So without delaying further, let’s begin!
Let’s quickly understand the sentence structure meaning.
What is sentence structure?
Sentence structure is how words are arranged in a sentence to express thoughts and ideas. It involves using parts of speech like nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, pronouns, conjunctions, and interjections.
To understand this sentence structure definition better, let’s see the various parts of a sentence.
Important parts of a sentence
The subject, verb, and object are important parts of sentences. Here is a simple explanation to understand these three parts:
Subject– The main focus of a sentence is the subject of the sentence. It can be a person, place, animal, thing, or idea.
Hina took an exam. (Subject- Hina)
Verb- The word that conveys action is the verb in the sentence.
He ran to the door. (Verb- ran)
Object- The person or thing that is impacted by the action is the object.
He broke the window. (Object- window)
The following example of sentence structure demonstrates all three concepts:
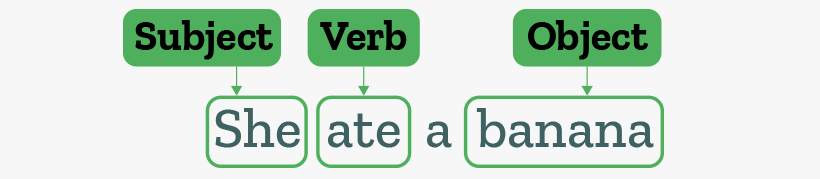
The above sentence clearly demonstrates the common sentence structure: Subject-Verb-Object (SVO). As objects are important parts of sentences, let’s quickly see the types of objects!
There are two types of objects, the direct object, and the indirect object.
Direct object- The person or thing that is directly affected by the action is the direct object. By asking the question “What?” or “Whom?”, you can understand the direct object.
She drove a car. (What did she drive? – a car)
He asked her. (Whom did he ask? – her)
Indirect object- The person or thing other than the direct object that also receives the action is the indirect object. It is indirectly affected by the action. Asking “To what?”, “To whom?”, “For what?”, and “For whom?” give us the indirect object.
John gave her a gift. (To whom did John give a gift? – her)
He returned the book to the library. (To what did he return the book?- the library)
She made pudding for the party. (For what did she make pudding?- the party)
Max played soccer for his son. (For whom did Max play soccer?- his son)
While these examples follow the Subject-Verb-Object (SVO) pattern, the structure of a sentence can vary. To understand English sentence structure better, let’s quickly understand the 4 basic rules to create sentence structures.
Sentence structure rules
1. Start every sentence with a capital letter.
2. At the end of every sentence, use a punctuation mark such as a full-stop, question mark, exclamation mark, or quotation marks.
3. All the connecting words used (e.g. and, because, if, when, who, which) must help to understand the subject of the sentence.
4. The verb and the subject must have the same form, meaning either both should be singular, or both should be plural. This is known as subject-verb agreement. For example:
Jim is not there. (Jim- Singular noun form, is- Singular verb form)
They are sincere and honest. (They- Plural noun form, are- Plural verb form)
Every sentence structure contains at least 1 clause. Hence, before seeing the types of sentence structure, let’s briefly understand clauses.
What are clauses and their types?
A clause is a group of words that include a subject and a verb. There are two types of clauses: independent clauses and dependent clauses.
1. Independent clause
Also known as the main clause, the independent clause contains a subject and a verb and expresses one single idea. It makes sense as a single sentence and doesn’t need any other clause to complete it.
Here is an example:
I read books.
The above sentence sounds complete and doesn’t need any additional words to clarify its meaning. The whole sentence “ I read books.” is an independent clause.
2. Dependent clause
Also known as the subordinate clause, the dependent clause contains more than one verb and expresses several ideas. It needs the independent clause to complete the sentence. Without the independent clause, the sentence feels incomplete and lacks clarity.
Here is an example:
I read books that inspire me to achieve my goals.
Here, the words “that inspire me to achieve my goals” is the dependent clause. Without the independent clause “I read books”, it would be difficult to understand the inspiration and the sentence would be incomplete.
Now that we know the basics of clauses, let’s understand the types of English sentence structure!
Types of sentence structure
The four main types of sentence structure are simple, compound, complex, and compound-complex.
1. Simple sentence
A sentence that has only one independent clause is called a simple sentence. It has only one verb and subject and expresses a single idea. For example:
I like painting.
She was very happy.
He went farther ahead.
2. Compound sentence
A sentence formed by joining two or more independent clauses is known as a compound sentence. The sentences are connected by using conjunctions like and, but, or, yet, so. They can also be linked by using punctuations like the semi-colon. Let us see some examples:
I went to the shop and I purchased some onions.
Ms. Martha knew the truth, but she couldn’t tell anyone.
We can go swimming on Friday; you can also bring your friend along.
3. Complex sentence
A sentence that consists of one independent clause and one or more dependent clauses is known as a complex sentence. Such sentences are usually linked using words like because, although, if, when, who, which, that.
Understand this structure in a sentence through the following examples!
Although it was cold, their son didn’t wear a warm jacket.
When I reach the airport, I will immediately call you.
Your mom realized who I was talking about and smiled.
4. Compound-complex sentence
A sentence that has two or more independent clauses and one or more dependent clauses is known as a compound-complex sentence. It is a combination of compound and complex sentences. Let us see some sentence structure examples to understand better.
I wanted to attend the meeting but I was unable to do so because of an emergency.
He said that he had a new red jersey which his wife had purchased, although I never saw him wearing it.
They knew that he was lying but couldn’t do anything about it because someone powerful was involved.
This concludes our guide about what is a sentence structure. Now, you can use these sentence structure types to communicate effectively. To improve sentence structure in written documents, it is essential to thoroughly edit them.
At PaperTrue, we provide expert editing and proofreading services to perfect your document. Whether you want to edit an academic or professional paper, we can help!
Here are some articles that you might find interesting:
Frequently Asked Questions